Nepal’s Economic Snapshot: Inflation Stays at 8.19%, Remittances Soar
KATHMANDU, [October 17 2023] – The latest economic indicators reveal a mixed bag for Nepal, with inflation holding steady, a drop in imports and exports, and a surge in remittances. Here’s a closer look at the country’s economic landscape for the first two months for 2080/81
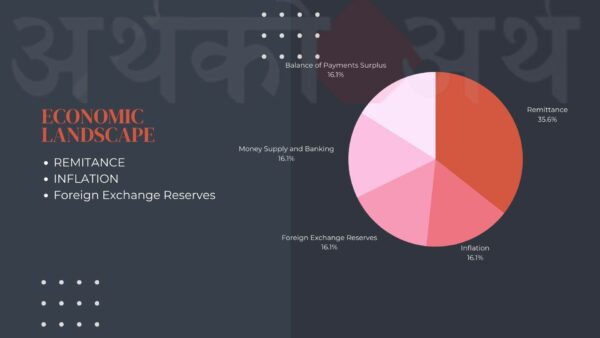
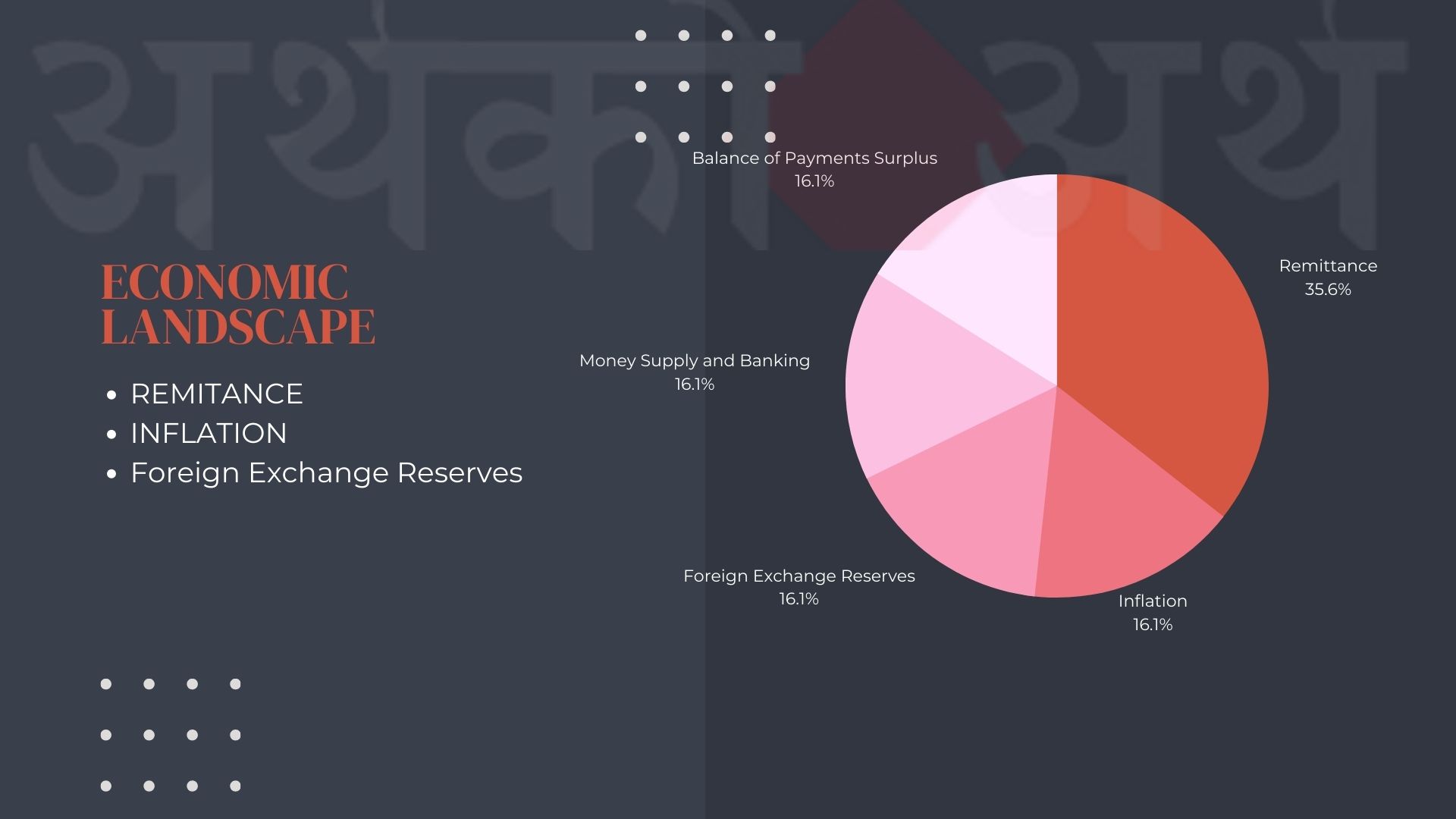
Inflation Maintains at 8.19%:
Consumer Price Index (CPI)-based inflation in Nepal has persisted at 8.19 percent year-on-year (y-o-y). The central bank’s efforts to stabilize prices seem to be having an impact, despite ongoing economic challenges.
Trade Deficit Narrows:
Nepal’s trade balance showed signs of improvement with imports decreasing by 5.1 percent and exports falling by 7.8 percent. This led to a 4.7 percent reduction in the trade deficit, which bodes well for the country’s economic stability.
Remittances on the Rise:
One of the standout highlights of the report is the substantial increase in remittances. In Nepalese Rupee (NPR) terms, remittances surged by 22.1 percent, and in USD terms, there was a remarkable 17.7 percent increase. This influx of funds from abroad is a harsh reality of nepali’s struggling to find the job here at their motherland
Balance of Payments Surplus:
Nepal continues to maintain a surplus in its balance of payments, with a surplus of NPR 53.61 billion, indicating that the country’s international transactions remain in good shape.
Foreign Exchange Reserves and Government Finances:
Gross foreign exchange reserves stood at NPR 1598.90 billion, equivalent to USD 12.01 billion. The Nepal government’s expenditure totaled NPR 131.14 billion, while revenue collection amounted to NPR 141.08 billion.
Money Supply and Banking:
Broad money (M2) experienced a slight decrease of 0.5 percent, but when viewed on a y-o-y basis, M2 displayed a notable 12.0 percent increase. Deposits at Banks and Financial Institutions (BFIs) saw a marginal 0.1 percent decrease, while private sector credit increased by 0.7 percent. On a y-o-y basis, deposits expanded by 13.2 percent, and private sector credit recorded a 4.0 percent growth.